
This forms the basis of the haemagglutination inhibition test used in the sero-diagnosis of influenza. HA agglutinates certain RBCs which is inhibited by the neutralizing antibodies.

HA enables the virus to absorb to muco-protein receptors on red cells as well as an respiratory epithelial cells.Haemagglutinin is one of the major antigen of influenza virus and is responsible for antigenic variation.The distal end which contains five antigenic sites (HA1-HA5) is responsible for binding of vision to host cells. The triangular shaped HA is inserted into the virus membrane by its tail end which is hydrophilic in nature.The Haemagglutinin consists of 500 spikes each measuring 12nm in length.These two polypeptides are joined together by disulfide bond. Haemagglutinin is a glycoprotein composed of two polypeptides- HA 1 and HA2, responsible for hemadsorption and haemagglutination.Haemagglutin derives its name from its ability to agglutinate erythrocytes under certain conditions.The M2 ion channel and the NS2 protein are also present in the envelope but a few copies per particle.The HA represents about 25% of viral protein the NA about 5%.These two surface glycoproteins are the important antigens that determine antigenic variation of influenza viruses and host immunity.They are synthesized in the early period of replication cycle, and get attached to the plasma membrane at specialized patches where budding occurs. These glycoproteins are triangular and mushroom shaped respectively.Two virus encoded glycoproteins, the haemagglutinin (HA) and the neuraminidase (NA) are inserted into the envelope and are exposed as spikes about 10mm long on the surface of the surface of the particles.The nucleocappsid is surrounded by an envelope which has an inner membrane of protein known as matrix or M protein which is virus encoded and outer lipid layer derived from infected host cell membrane during the process of replication by budding.The matrix (M1) protein which forms a shell underneath the viral lipid envelope is important in particle morphogenesis and is a major competent of the virion.Three large proteins (PB1, PB2, and PA) are bound to the viral Ribonucleoprotein and are responsible for RNA transcription and replications.Also contains a viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase that transcribes the negative polarity genome into mRNA.

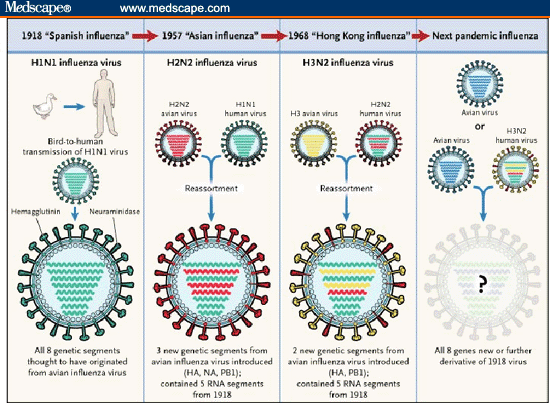
This phenomenon call genetic re-assortment, may result in sudden changes in viral surface antigens- a property that explains the epidemiological features of influenza and poses significant problems for vaccine development.
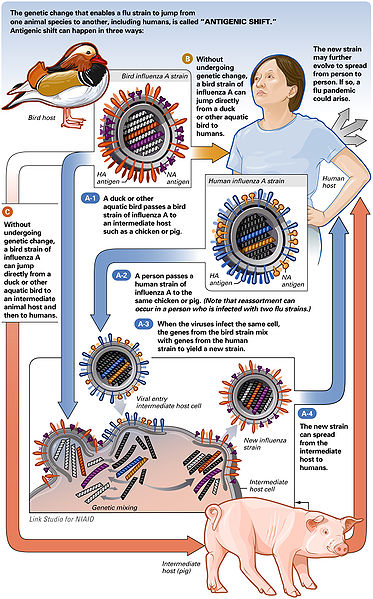
Influenza virus type A and less in type B, while it has not been demonstrated (Haemagglutinin and Neuraminidase) show variations and are primarily
They cause influenza, an acute infections disease Influenza viruses areĬlassic respiratory viruses. Genus Influenza virus with three types-A, B and C.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
